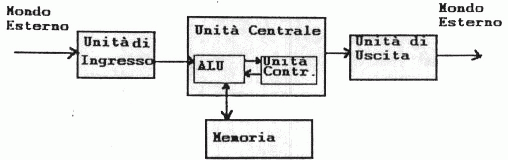
Con il termine “architettura di Von Neumann” si intende uno schema progettuale di calcolatori elettronici inventato dal matematico John Von Neumann nel 1951.
La struttura da lui inventata era costituita da tre componenti fondamentali, a cui andavano ad aggiungersi altre periferiche collegate tramite un modulo di input/output.
I tre componenti fondamentali sono:
- La CPU che si occupa di eseguire le istruzioni che vengono scritte in linguaggio macchina e risiedono nella memoria RAM. Si divide in due parti fondamentali: l’unità di controllo e la ALU, cioè l’unità di calcolo.
- La Memoria in cui risiedono i dati e le istruzioni scritti in linguaggio macchina.
- Il BUS, cioè un collegamento fisico (costituito da un cavo elettrico) tra la memoria, la CPU e gli altri componenti del calcolatore; permette lo scambio di informazioni grazie all’invio di impulsi elettrici.
Tuttavia il modello di Von Neumann prevede anche la presenza di periferiche che permettono l’utilizzo del calcolatore: ad esempio il mouse, la tastiera, il monitor.
Queste dialogano con il processore tramite i moduli di Input (i dati vengono inseriti nel calcolatore per essere elaborati) e Output (i dati che vengono restituiti all’operatore) che vengono collegati al bus.

The term "Von Neumann architecture" means a design scheme of electronic computers invented by mathematician John von Neumann in 1951. The structure invented by him was made up of three basic components, which were additional to other devices connected via a form of input / output. The three basic components are: The CPU is responsible for executing instructions that are written in machine language and reside in RAM memory. It is divided in two basic parts: the control unit and the ALU, namely the calculation unit. The memory in which the data resides, and instructions written in machine language. The BUS, ie a physical link (constituted by an electrical cable) between the memory, the CPU and other components of the computer, allows the exchange of information by sending electrical pulses. However, the Von Neumann model also includes the presence of devices that allow the use of the computer: for example, a mouse, a keyboard, monitor. These communicate with the processor through the forms of input (the data are entered into the computer to be processed) and output (the data that is returned to the operator) that are connected to the bus.